Glucose transporters are required from shuttling glucose from the extracellular to intracellular compartment. Insulin by binding to the tyrosine kinase insulin receptor present on target cells promotes the translocation of various sodium glucose transporters from the Golgi apparatus to the cellular membrane.
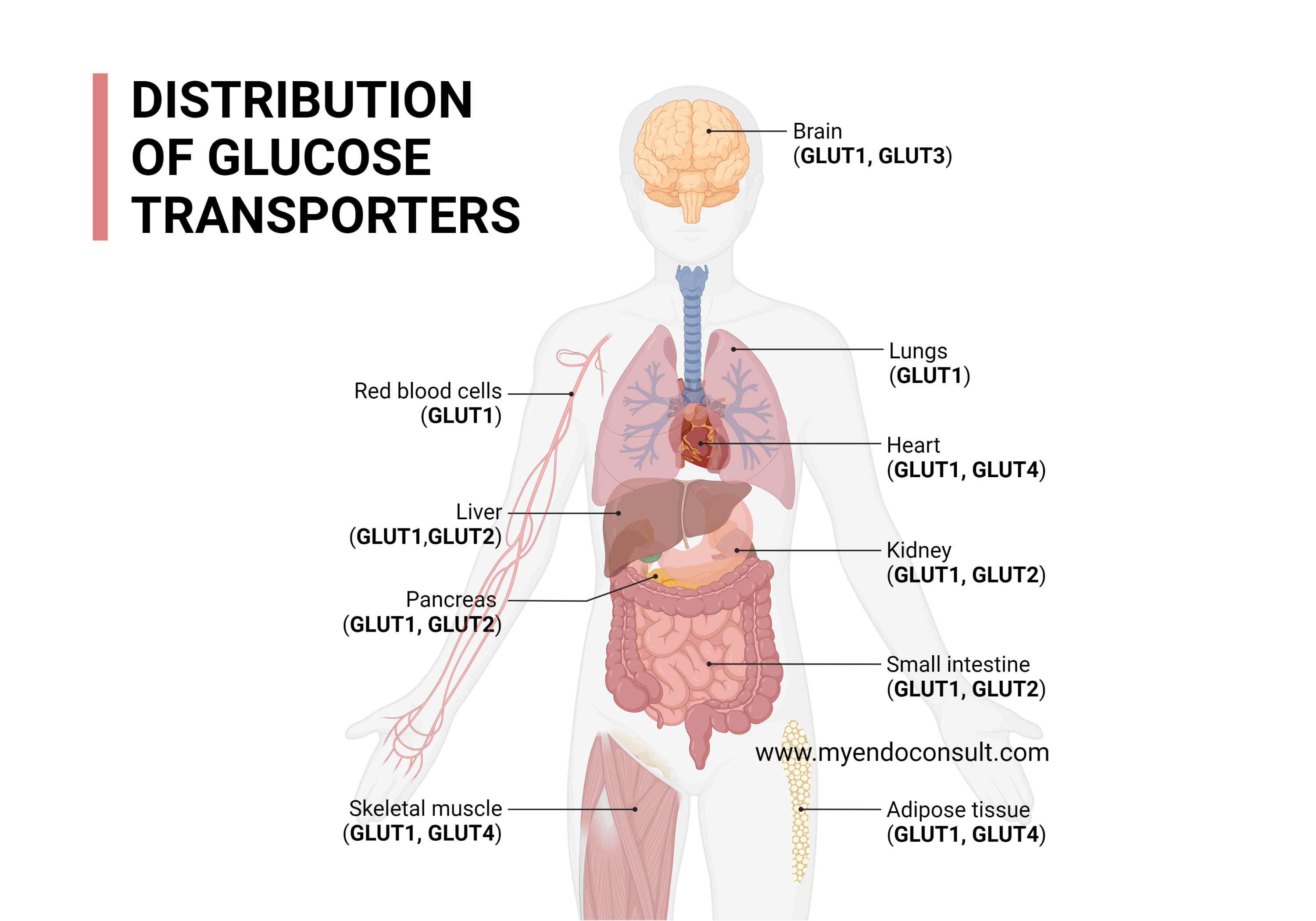
Location of Glucose Transporters
The distribution of glucose transporters varies significantly between various tissues. Insulin is not required for the expression of all glucose transporters. For example, GLUT-2 transporters present in pancreatic islet (beta) cells and hepatocytes are insulin independent. On the other hand, GLUT-4 transporters present in striated muscle and adipose tissues, are insulin dependent and are induced in response to the presence of insulin.
| Glucose Transporter | Location | Comments |
| GLUT-1 | Erythrocytes, blood-brain barrier | Low level of basal glucose uptake required to sustain cellular respiration |
| GLUT-2 | Beta cells, renal tubular cells, liver, intestinal epithelial cells | |
| GLUT-3 | Neurons and placenta | |
| GLUT-4 | Striated muscle and adipose tissue | ONLY insulin-regulated GLUT : It is responsible for insulin mediated glucose uptake |
We found this detailed lecture by AK Lectures (on YouTube) very helpful. Watch this video if you are interested in learning more about the properties of Glucose Transporters.
Kindly Let Us Know If This Was helpful? Thank You!


