The endocrine system plays a vital role in maintaining the body's delicate balance through the production and release of hormones. These chemical messengers regulate various physiological processes, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. We will take a closer look at the histology of various endocrine glands, including the pituitary gland, parathyroid glands, thyroid gland, pancreas, testis, ovaries, and adipose tissue.
The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and growth. Its primary function is to produce thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The thyroid gland is composed of spherical structures called follicles, which are lined by follicular cells responsible for hormone production. Between the follicles are parafollicular cells (C cells), which secrete calcitonin, a hormone involved in calcium homeostasis.
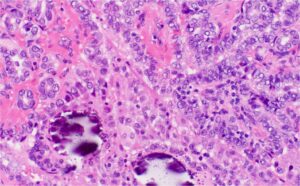
Histology of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common type of thyroid cancer,
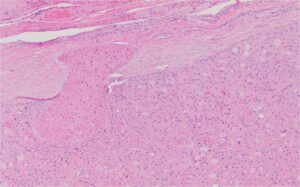
Histology of Hurthle Cell Adenoma and Carcinoma
Hurthle Cell Adenoma Hurthle cell adenoma is a rare, benign tumor of
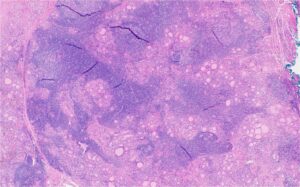
Histology of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disorder
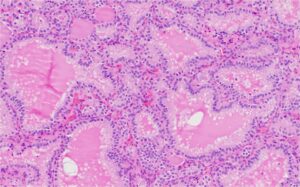
Histology of Graves Disease
Graves' disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland, leading

Follicular Carcinoma Histology
Follicular carcinoma is the second most common type of thyroid cancer, accounting
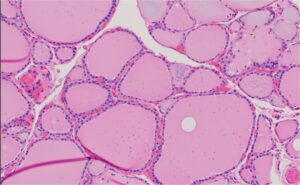
Normal Thyroid Follicular Cells
Normal thyroid follicular cells, also known as thyrocytes, are the primary cell
University of Minnesota Medical School. Residency in anatomic and clinical pathology and fellowship in cytopathology at Mayo Clinic School of Graduate Medical Education in Rochester, Minnesota.
- PAUL LAPPINGA (PATHOLOGIST, SANFORD HEALTH)
Kindly Let Us Know If This Was helpful? Thank You!

