Adrenal Vein Sampling Procedure and interpretation
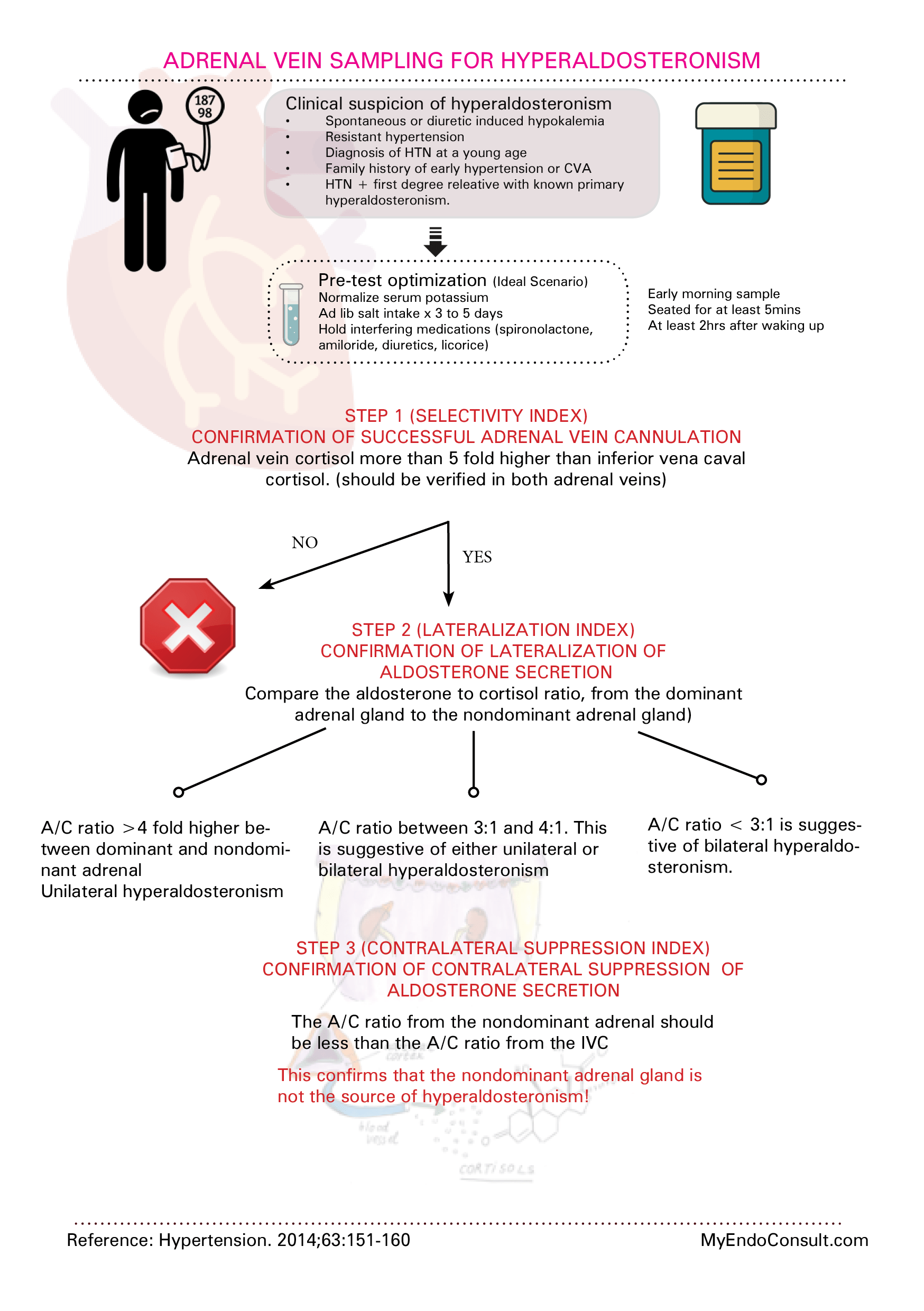
AVS involves the sequential catheterization of both adrenal veins and the collection of blood samples, which are later assayed for adrenal hormones. The procedure is typically performed with the guidance of fluoroscopy to ensure accurate positioning of the catheter. The left adrenal vein is more technically challenging to catheterize due to its short, direct entry into the renal vein.
Cortisol levels are measured as a surrogate marker to confirm successful cannulation of the adrenal veins. The results are typically expressed as a selectivity index (SI), which is the ratio of cortisol concentration in the adrenal vein to that in the inferior vena cava or renal vein. An SI greater than 2 is generally considered to confirm successful cannulation.
Once successful catheterization is confirmed, adrenal hormone levels, such as aldosterone and cortisol, are measured. The lateralization index (LI), which compares the aldosterone-to-cortisol ratio between the two adrenal veins, is used to identify unilateral from bilateral disease. A LI greater than 4 is usually indicative of unilateral disease.
Localization of source of hyperaldosteronism (Adrenal Vein Sampling)
Kindly Let Us Know If This Was helpful? Thank You!


