Levothyroxine Absorption Test (Infographic)
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone, thyroxine (T4), and is the standard treatment for hypothyroidism. In some cases, patients may experience difficulty in achieving therapeutic levels of thyroid hormones despite taking appropriate doses of levothyroxine. The levothyroxine absorption test is a diagnostic tool used to identify the cause of poor levothyroxine absorption and to guide subsequent treatment adjustments. This article provides an overview of the levothyroxine absorption test, including its methodology, clinical indications, and implications for patient care.
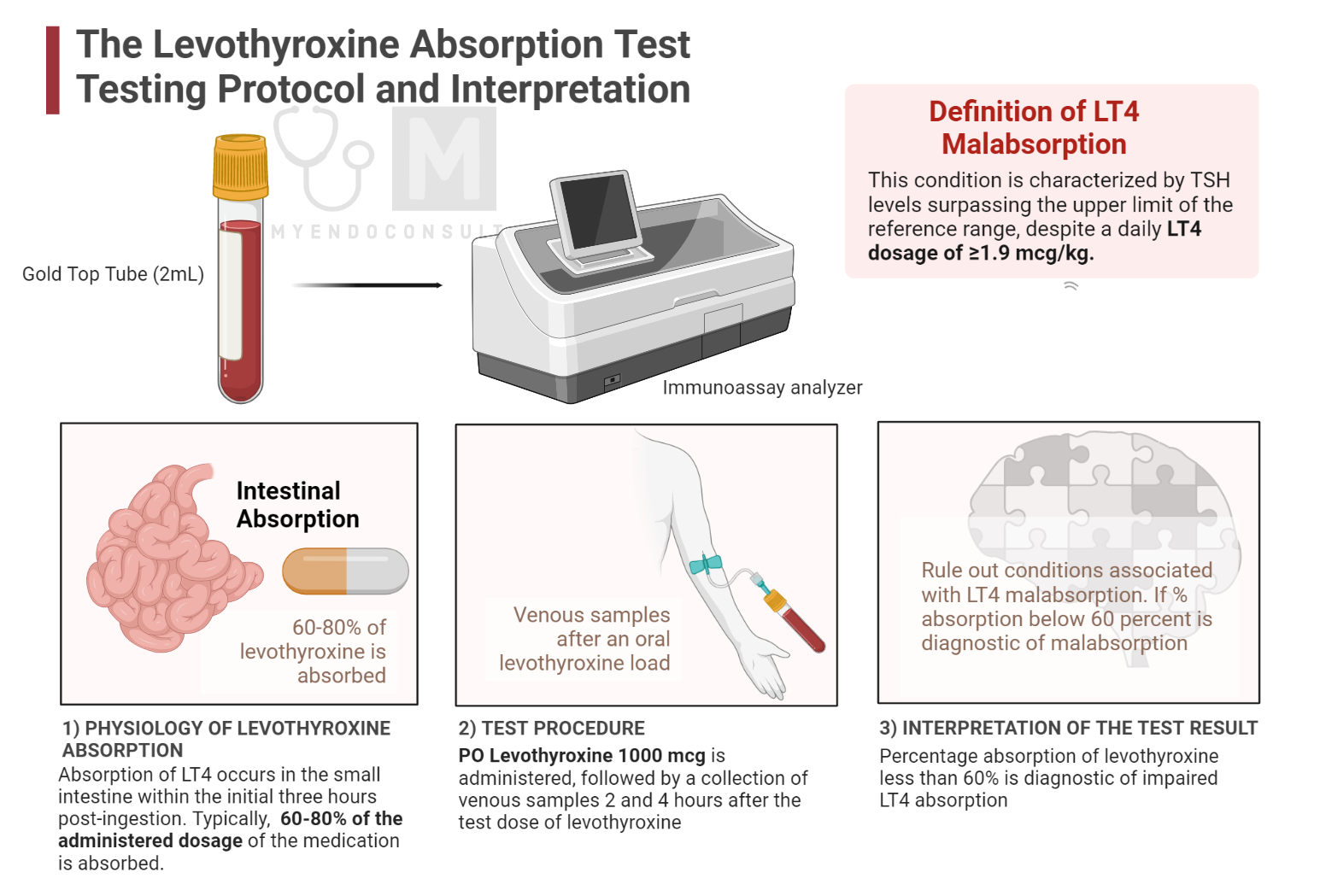
Absorption predominantly transpires in the small intestine within the initial three hours post-ingestion. Typically, only 60-80% of the administered dosage of the medication is absorbed.
Conventional LT4 dosing is conducted through a weight-based calculation, with the majority of patients necessitating 1.6 to 1.8 mcg/kg to attain thyrotropin (TSH) concentrations within the reference range.
Although most patients exhibit favorable outcomes with this treatment, a minor subset of individuals display persistent hypothyroidism despite receiving considerable LT4 dosages, a phenomenon referred to as refractory primary hypothyroidism.
This condition is characterized by TSH levels surpassing the upper limit of the reference range, despite a daily LT4 dosage of ≥1.9 mcg/kg.
Methodology
The levothyroxine absorption test evaluates a patient's ability to absorb levothyroxine by measuring serum T4 levels before and after the administration of a test dose of levothyroxine. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- A blood sample is collected to measure the patient's baseline serum T4 level.
- The patient is given a test dose of levothyroxine, usually 1,000 mcg, taken orally on an empty stomach.
- A second blood sample is collected 2 to 4 hours after the test dose to measure the serum T4 level.
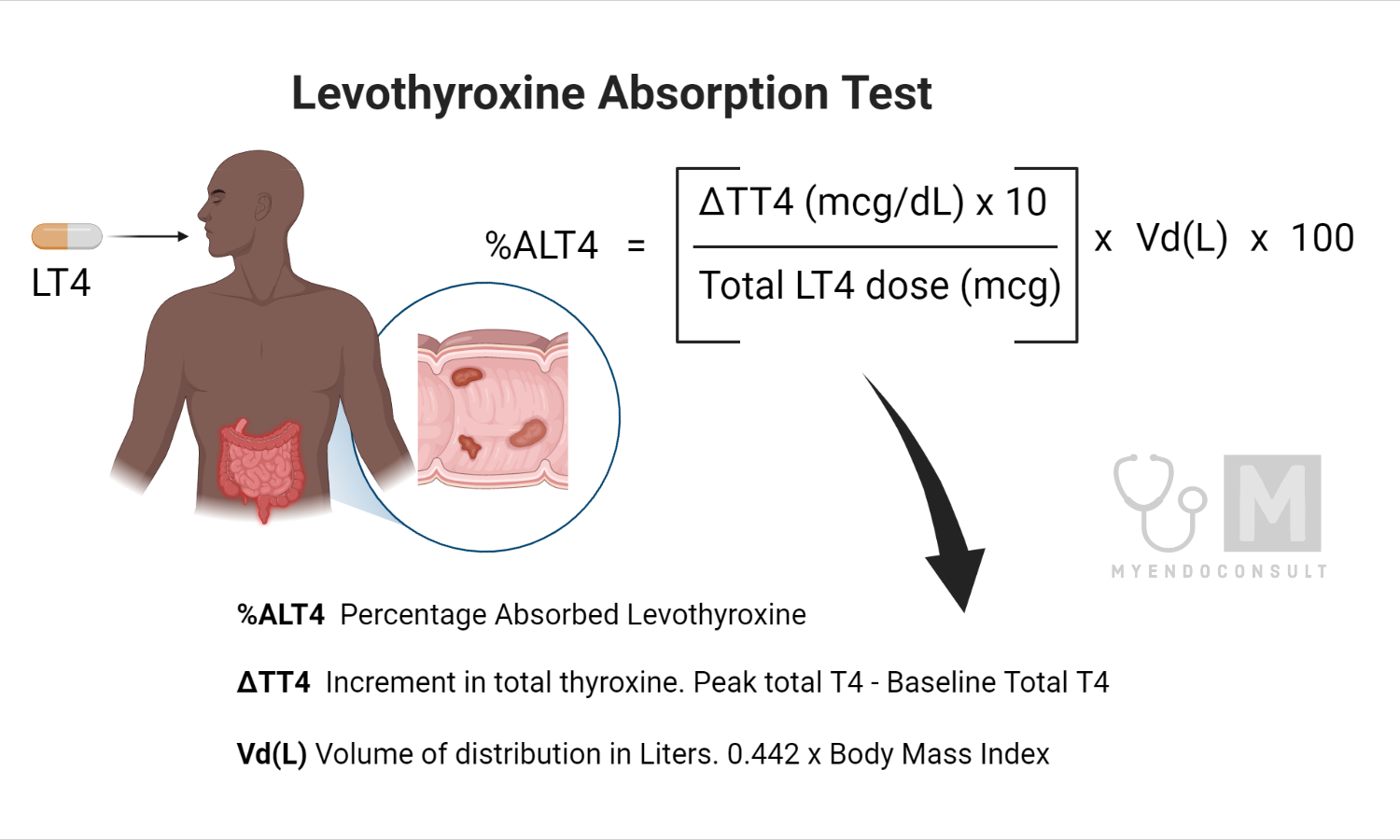
- The percentage of levothyroxine absorption is calculated by comparing the baseline and post-dose T4 levels
Clinical Indications
The levothyroxine absorption test is indicated for patients with hypothyroidism who experience difficulty achieving therapeutic levels of thyroid hormones despite taking appropriate doses of levothyroxine. This test may be particularly useful for patients with:
Gastrointestinal disorders
Conditions such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or gastric bypass surgery can impair the absorption of levothyroxine.
Drug interactions
Certain medications, including proton pump inhibitors, calcium supplements, and iron supplements, can interfere with levothyroxine absorption.
Compliance issues
Patients who are suspected of not taking their medication as prescribed may benefit from the levothyroxine absorption test to determine the cause of suboptimal treatment response.
Implications for Patient Care
The levothyroxine absorption test can provide valuable information to guide treatment adjustments for patients with hypothyroidism who struggle to achieve therapeutic levels of thyroid hormones. Based on the test results, healthcare professionals may consider the following interventions:
Patients with reduced levothyroxine absorption may require higher doses to achieve therapeutic levels. If an underlying gastrointestinal condition is identified, treating the disorder may improve levothyroxine absorption.
For patients with drug interactions, adjusting the timing of levothyroxine and interacting medications or considering alternative treatments may enhance levothyroxine absorption. In cases of poor compliance, healthcare providers can counsel patients on the importance of taking levothyroxine as prescribed and discuss strategies to improve adherence.
Conclusion
The levothyroxine absorption test is a valuable diagnostic tool in identifying the cause of poor levothyroxine absorption in patients with hypothyroidism. By understanding the factors that contribute to malabsorption and tailoring treatment accordingly, healthcare professionals can optimize thyroid hormone levels and improve patient outcomes.
Kindly Let Us Know If This Was helpful? Thank You!


