This mnemonic is an updated version of a memory device published in a paper titled “A practitioner’s simple mnemonic for managing diabetes”: GLUCOSE BAD.”
G = Glycemic control
A1C, Blood glucose monitoring (BGM) based on capillary glucose, or Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) based on interstitial glucose.
Assess glycemic status at least two times a year in patients meeting treatment goals. Assess these parameters at least every three months for those not meeting glycemic goals.
| Measure | Target |
| A1C | <7.0% (53 mmol/mol) |
| Preprandial capillary plasma glucose | 80–130 mg/dL |
| Peak postprandial capillary plasma glucose | <180 mg/dL |
| Time in range | >70% |
| Time below range | <4% |
| Time below <54mg/dL | <1% |
- For example, less stringent goals, A1C <8.0%, maybe appropriate for patients with several comorbidities or limited life expectancy.
- More stringent goals, such as A1C <6.5% (48 mmol/mol) for women planning a pregnancy, reduce the risk of pre-eclampsia, fetal macrosomia, preterm delivery, and congenital anomalies.
L –LIPIDS
Primary prevention
- Diabetes, aged 40-75 years without ASCVD (moderate-intensity statin)
- Diabetes, aged 20-39 years with additional ASCVD risk factors (consider statin in addition to lifestyle changes)
- Diabetes, aged 50-70 years with multiple ASCVD risk factors (high-intensity statin)
- Diabetes, 10-year ASCVD risk factor of 20% or greater (Add ezetimibe to a maximally tolerated statin to reduce LDL cholesterol by 50% or more)
Secondary prevention
- Diabetes, irrespective of age, with established ASCVD (high-intensity statin)
- Diabetes established ASCVD, LDL ≥70 mg/dL on maximally tolerated statin dose, consider adding additional LDL-lowering therapy (such as ezetimibe or PCSK9 inhibitor)
Other lipoprotein fractions
- Fasting triglyceride >500mg/dL should be evaluated for secondary causes of hypertriglyceridemia. Treat to reduce the risk of acute pancreatitis.
- For patients with ASCVD or other CV risk factors on statin therapy, controlled LDL cholesterol but elevated fasting triglycerides (135-499mg/dL), add icosapent ethyl to reduce the risk for CV events.
U–Urine microalbuminuria
- Chronic kidney disease attributable to diabetes (DKD) develops after at least 10 years of type 1 diabetes mellitus but may be present at the time of diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. To establish a diagnosis of albuminuria, at least 2 to 3 urine samples (urine albumin creatinine ratio) should be collected within a 3 to 6 month period before considering treatment.
- Optimize glycemic control to slow the progression of DKD
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus with eGFR ≥25 mL/min/1.73 m2 and urinary albumin ≥300 mg/g creatinine, an SGLT-2 inhibitor is recommended to prevent the progression of the disease.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus with eGFR ≥25 mL/min/1.73 m2 and urinary albumin ≥300 mg/g creatinine (increased risk of CKD progression) who are unable to tolerate SGLT-2 inhibitors, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (finerenone) is recommended. [FIDELIO-DKD clinical trial infographic].
- In Diabetes, nondialysis-dependent stage 3 or higher CKD, dietary protein intake should be a maximum of 0.8 g/kg body weight per day.
- Diabetes, urinary albumin ≥300 mg/g creatinine and/or an eGFR 30–60 mL/min/1.73 m2should be monitored every six months
C–Cigarettes
- Advise against the use of conventional cigarettes, e-cigarettes, or other tobacco products. Smoking cessation counseling and treatment as part of a comprehensive diabetes management plan.
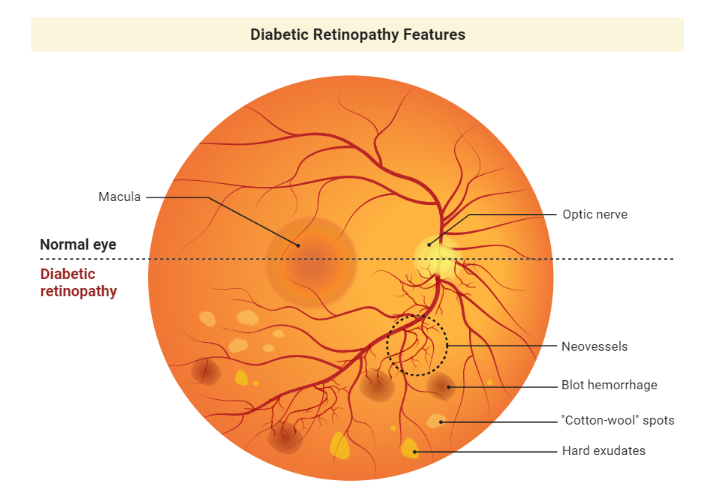
O–Ophthalmology
- For patients with type 2 diabetes, an initial dilated and comprehensive eye examination at the time of diagnosis is recommended. If there is no evidence of retinopathy, screening every 1-2 years may be considered. If diabetic retinopathy is present, yearly dilated eye examinations are required.
- For all pregnant women with diabetes (1 or 2) dilated eye exam should occur ideally before pregnancy or in the first trimester, and then at least ONCE every trimester and again one year postpartum.
S- Sexual, Psychosocial, and Diabetes distress
- Screen for sexual dysfunction (both men and women), depression, anxiety, and disordered eating. Diabetes distress is defined as significant adverse psychological reactions related to emotional burdens and worries specific to an individual’s experience managing a severe, complicated, and demanding chronic disease such as diabetes.
E – Extremities
- Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy is recommended at least annually in all patients, starting at the time of diagnosis for type 2 diabetes and at five years after diagnosis in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Assessment of distal symmetric polyneuropathy requires the use of either temperature or 10g monofilament (small fiber function) and vibration sensation using a 128-Hertz tuning fork (large-fiber function)
B – Blood pressure
- Blood pressure targets should be individualized through a shared decision-making process that addresses CV risk, potential adverse effects of antihypertensive medications, and patient preferences
- Diabetes and hypertension at higher CV risk (existing ASCVD or 10-year ASCVD risk ≥15%), a blood pressure target of <130/80 mmHg
- Diabetes and hypertension at lower risk for CVD (10-year ASCVD risk <15%), treat to a blood pressure target of <140/90 mmHg.
A = Aspirin
- Antiplatelet drugs in diabetes mellitus
- Aspirin therapy (75–162 mg/day) may be considered a primary prevention strategy in those with diabetes who are at increased CV risk
D = Dental examination
Periodontal disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in patients with diabetes mellitus. Periodontal disease also sets up a vicious cycle of continuous inflammation, which consequently worsens insulin resistance.

References
- American Diabetes Association; Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin Diabetes 1 January 2022; 40 (1): 10–38
- Ziliotto McCrudden, J. G., & Hull, B. J. (2015). A Practitioner’s Simple Mnemonic for Managing Diabetes: “GLUCOSE BAD.” The Journal for Nurse Practitioners, 11(4), 451–455.
Images(s) Courtesy
MyEndoConsult
Kindly Let Us Know If This Was helpful? Thank You!


