STEP 1 : Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity
STEP 1 : Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity
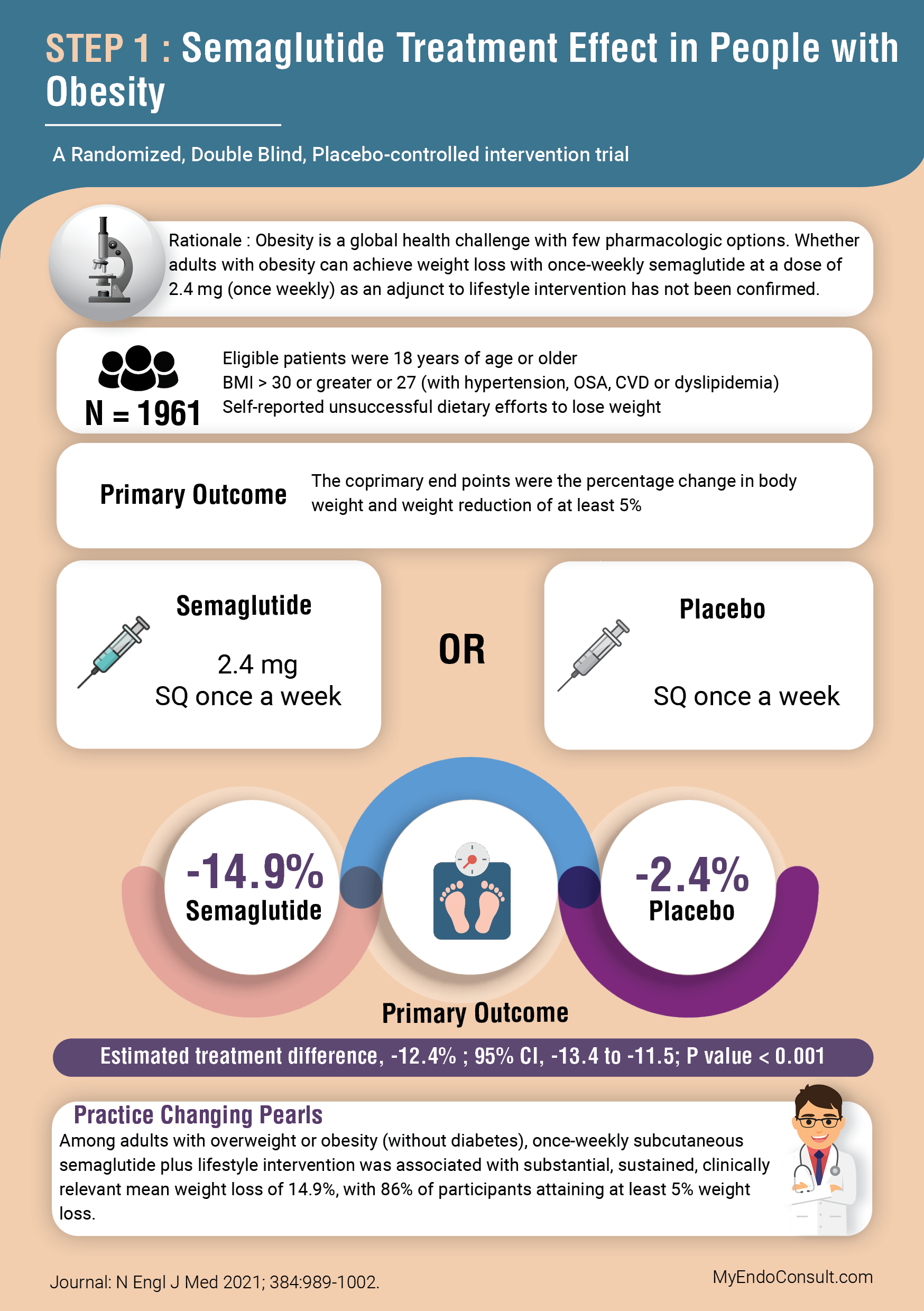
Rationale : Obesity is a global health challenge with few pharmacologic options. Whether
adults with obesity can achieve weight loss with once-weekly semaglutide at a dose of
2.4 mg (once weekly) as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention has not been confirmed.
Abstract
Participants
Eligible patients were 18 years of age or older
BMI > 30 or greater or 27 (with hypertension, OSA, CVD or dyslipidemia)
Self-reported unsuccessful dietary efforts to lose weight
Outcome
The coprimary endpoints were the percentage change in body weight and weight reduction of at least 5%
Semaglutide 2.4 mg SQ once a week versus Placebo. Estimated treatment difference, -12.4% ; 95% CI, -13.4 to -11.5; P value < 0.001
Practice Changing Pearls
Among adults with overweight or obesity (without diabetes), once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide plus lifestyle intervention was associated with substantial, sustained, clinically relevant mean weight loss of 14.9%, with 86% of participants attaining at least 5% weight loss.
Infographic
Reference
Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, Davies M, Van Gaal LF, Lingvay I, McGowan BM, Rosenstock J, Tran MTD, Wadden TA, Wharton S, Yokote K, Zeuthen N, Kushner RF; STEP 1 Study Group. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021 Mar 18;384(11):989-1002.
